What is it?
Many of the technologies used in our everyday lives require some sort of heat management. Common types include fans blowing air on equipment to cool it (think a PC or laptop), fans blowing air over coils (think outdoor air conditioning units or industrial cooling towers), or metal fins attached to a hot surface (think of the base of an industrial LED fixture). Proper heat management affects the equipment life and efficiencies of these applications. A new technology called radial flow heat exchangers (also called Radial Sandia Coolers) improve heat management over traditional methods, improving efficiency and equipment life.

How does it work?
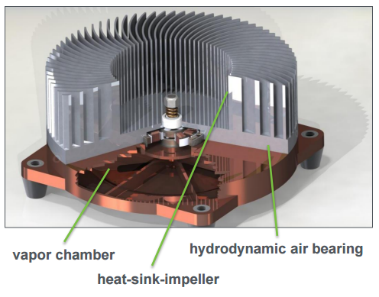
Radial flow heat exchangers consist of a baseplate, a circular finned heat exchanger, and a small brushless DC motor. The circular heat exchanger sits on top of the baseplate (see picture), and the motor rotates the fins at 2,000-3,000 RPM. The rotation of the curved fins vastly improves the heat transfer capabilities of the heat exchanger over traditional methods.
What are the most appropriate applications?
Currently, this technology is being explored for computers, data centers, and A/V equipment where small, intense sources of heat must be dissipated quickly. It is also being explored for LED lighting. Future applications include air-conditioning and refrigeration systems.
What are the savings?
Savings over traditional heat management using fan cooling can be 40-80%, depending on the application. With LED lighting, radial flow heat exchangers have proven to be up to 10x better at managing heat than current methods which improves operation and equipment life in higher temp environments (like high-bay industrial settings). For refrigeration, research shows that this technology can generate a 50% improvement in heat transfer, which could improve the efficiency (COP) of refrigeration systems by as much as 10%.
What are the non-energy benefits?
The fins rotate so quickly that they do not get fouled as easily with dust and dirt as other fans. For LED fixtures, the better heat management can double fixture life and make LEDs more suitable for higher temperature environments.
What is the status/availability of the technology?
This technology is starting to be used in computer and data center applications, but is still being researched for lighting, air-conditioning, and commercial/industrial refrigeration.
What kinds of incentives/programs are available?
This technology would be evaluated under Custom programs.



